
COLD FORGING AND COLD HEADING
FINECS’ cold forging and heading processes are advanced forming technologies that shape metal at room temperature without heating. By preserving the material’s fiber structure during processing, we achieve superior mechanical strength and durability in the finished parts. In addition, this method minimizes material waste, offering significant benefits in terms of environmental impact and cost efficiency.
With decades of experience and proprietary die technology, we can handle extremely fine and complex shapes, making our solutions ideal for a wide range of applications, including automotive components, electronic devices, and industrial equipment.
Core Technology: Heading (Cold Forging)
Heading is a type of plastic forming process that shapes metal by applying force—such as striking, stretching, or bending—without cutting. Techniques include shearing, forward extrusion, upsetting, and backward extrusion. Compared to machining methods that remove material to achieve the desired shape, heading enables high-speed, high-volume production, delivering substantial advantages in cost reduction and value engineering.
cold forging- Product List
-
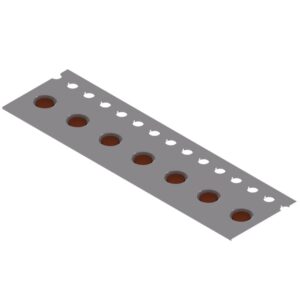
Embossed Taping (terminal pins & tiny components)
Can be mounted directly onto the PCB
-
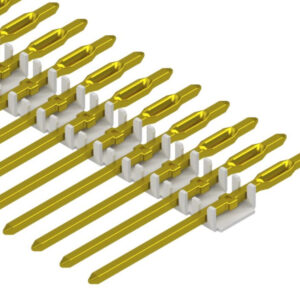
Press-fit bandolier terminals
Ensures a consistent insertion orientation for terminals
-

Deep drawn pins / cups
Components featuring cup-shaped terminals or pins
-

Pyramidal pins
Processed by cold forging into a pyramidal shape
-
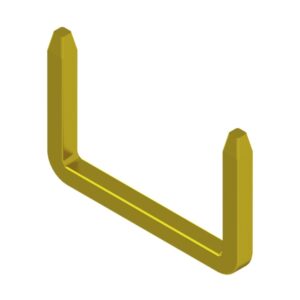
U-shaped pins Pyramidal pins
Used as jumper wires
-

Crank-shaped pins Pyramidal pins
Pyramidal tapers on both ends with a crank bend in the middle
-
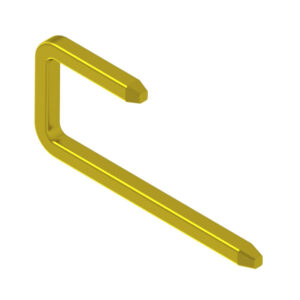
J-shaped square pins
Processed by cold forging into a shape resembling the number 7
-

L-shaped pins Pyramidal pins and cross-shaped cross sections
Flattening combined with a right-angle bend
-

Swaged L-shaped pins Pyramidal pins and cross-shaped cross sections
Connector and transformer terminals
-

„ear-crush“ flat square with pyramid taper
Flattened section that retains part of the original wire diameter.
-

Swaged straight pins Pyramidal pins and cross-shaped cross sections
Pin with one end rounded
-

Straight pins Pyramidal pins and cross-shaped cross sections
A flattened middle section featuring diagonal protrusions
-

Partially pinched straight pins Pyramidal pins
Flattened in the middle while retaining part of the original wire diameter
-

Partially flattened straight pins Pyramidal pins
Pyramidal taper with a flattened section in the middle
-
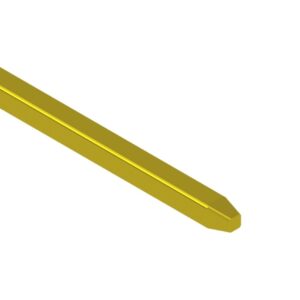
Straight pins Pyramidal pins
Square wire with pyramidal tapers on both ends
-

Mid-flanged straight pins with conical tapers
Conical tapers on both ends with a collar formed in the middle
-

Straight pins with conical tapers and cross-shaped cross sections
Flattened in the middle with protrusions extending in a cross direction
-

Partially pinched straight pins with conical tapers
Flattened in the middle while retaining part of the original wire diameter
-

Partially flattened straight pins with conical tapers
Cone-shaped taper with a flattened section in the middle
-

Straight pins with 4-side tapers from round wires
Round wire with four tapered surfaces applied to both ends
-

Straight pins with conical tapers from round wires
A component made from round wire featuring conical tapers on both ends
-

Partially flattened straight pins with round chamfers
A part with barrel-chamfered ends and a flat crimp in the middle
-

Partially pinched straight pins with round chamfers
A part with barrel-chamfered ends and a flattened crimp in the middle
-
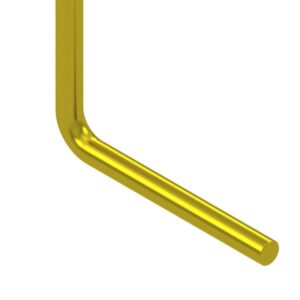
L-shaped pins (right angle)
A part with a right-angle bend in the middle
-

Double-step L-shaped pins
A part with two right-angle bends in the middle
-

U-shaped pins
A part with a U-shaped bend in the middle
-
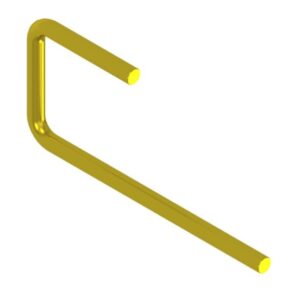
J-shaped round pins
A part with two or more bends in the middle
-

Partially flattened L-shaped pins
A part with a right-angle bend and a flat crimp in the middle
-

High-volume Pins
Single header pin with an exceptionally large flange
-

L-shaped pins Pyramidal pins
A part with tapered pyramidal ends and a right-angle bend in the middle
-

Mid-flanged straight pins Pyramidal pins
A component with tapered pyramidal ends and a flange in the middle
-

Mid-flanged straight pins with round chamfers
Featuring barrel chamfering on both ends and a flange in the middle
-

Needle-eye square press-fit
Featuring a needle-eye shaped design.
-
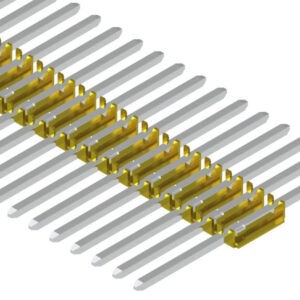
Bandolier terminals / pins made from square or flat square wires
Ensures a consistent insertion direction for terminals
-

Bandolier terminals / pins made from round wires
Ensures a consistent insertion direction for terminals
-

Crank shaped pins
Featuring crank bends in the middle section
-

End-to-end pins / End-to-end terminals (press-fit type)
Continuous pins with press-fit terminal shapes
-
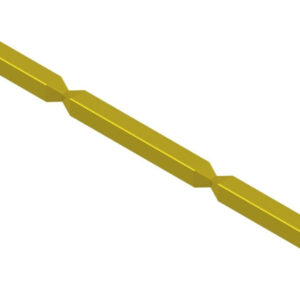
End-to-end pins / End-to-end terminals (square type)
Delivered on reels without cutting each piece, keeping them connected
-

End-to-end pins / End-to-end terminals (round type)
Delivered on reels without cutting each piece, keeping them connected
-
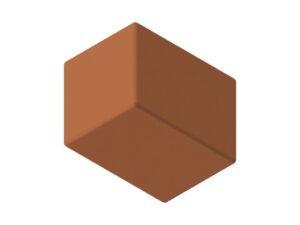
Block terminals (heat dissipation terminals and block pins)
Cylindrical or rectangular terminals and pins
-

Terminals with solder
A product with solder bonded at the center of the header surface
-

Heat radiating pins for heat sinks
Designed for applications like heat sinks to disperse and release heat effectively.
-

Rivet (Pin holder, Terminal holder)
Allows placement at any position on the board without drilling holes.
-

Hollow Rivet
This component is used for fastening (crimping) metal plates and profiles.
-

PGA Pins (Terminals for CPUs)
Electrically connects the CPU package substrate to the socket on the motherboard
-

Connector terminals / Connector pins
Various Shapes Achieved Through Our Proprietary Cold Forging and Header Processing Technologies
-

Lead pins / Diode terminals
An electronic component with rectifying properties
-

Jumper pins
Used on substrates
-

Press-fit terminals (from wire)
Eliminates the soldering process and contributes to reducing environmental impact.
-

Substrate terminals / Post pins
Compatible with a wide range of boards, such as ceramic and alumina types.
-

Antenna Pins
Plastic working of shape-memory alloys requiring specialized technology
-

Quartz resonator terminals (hermetic seal terminals)
Features hermetic sealing
-

Conductive terminals
Used in diodes, LEDs, semiconductors, and CCFL cold cathode tubes
-

Kovar pins (electrode pins)
Cuts the edge angles and fracture surfaces using a proprietary method
-

Leadless diode terminals / Dumet pins
High-speed switching, miniature bulbs, and LEDs
-
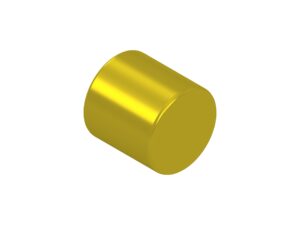
Brazing filler metal cut pieces (gold, silver, copper, etc.)
Wire brazing alloys cut to specified lengths
-

Ultra-small pins, extra-fine pins, micro pins
Used for connecting semiconductor chips to package interposers
-

Plungers for Contact Probes
Eco-friendly because it does not generate chips due to cutting process.
-
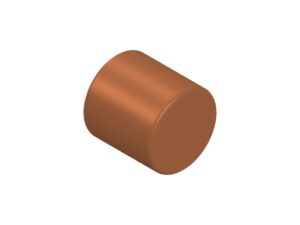
Copper Pillar pin
Optimum for circuit connection of advanced packaging design
-

Copper inlay
Enables thermal management to maintain electronic component performance and extend product lifespan.
-

Electrode Terminals of Rechargeable Battery
Positive and negative terminals for next-generation vehicles.
