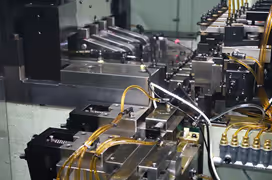
What is Cold Forging?
What is Cold Forging?
Cold forging is a processing technology that changes shape by applying pressure at room temperature without heating metal. This method improves the internal structure of the metal and increases the strength and accuracy of the product. This page provides detailed information on the advantages of cold forging, as well as applications in various industries. Cold forging is used in a wide range of fields, including the automobile industry, aerospace industry, and construction industry. Especially in the manufacturing of parts that require high strength and precision, it is an indispensable processing technology.
Know how to process
This section describes in detail the general process of cold forging. Cold forging is mainly performed in the following steps. ① Preparation of materials: Choose the proper metal material and cut if necessary. ② Forging: Use a special press to apply pressure to the metal to get the desired shape. ③ Finishing: Carry out finishing operations such as deburring and polishing of forged parts as needed.
Characteristics of each processing method
Forging and Pressing
In the plastic working of metallic materials, "forging" and "pressure forming" are used in the same sense as forging, pressure forming, etc. "Forging" is used to obtain the desired shape by applying a large pressure to the material. In addition to obtaining the desired shape, the term "forging" is often used when it is meaningful to increase the strength in combination with the shape deformation, and "press forming" is often referred to as header forming. This is a machining method that is mainly used to obtain the shape like the head of a screw (head). As mentioned above, the press forming and forging are used in almost the same sense. However, the method of deforming the material by applying pressure from the lateral direction is the press forming method, and the method of deforming the material by applying pressure in the vertical direction is generally the forging method.
Cold forging and hot forging
The forging and forging processes are classified by the temperature of the material used in the forging process. In addition to cold forging and cold forging using ordinary-temperature materials, there are also hot, hot, and hot forging methods for hot working. Each of them has advantages and disadvantages, so it is necessary to select the machining method depending on the product application. Among the processing methods described below, we offer products for cold forging and cold forging.
Cold forging and cold forging
>Advantages: High precision, high processing speed, smooth surface
>Disadvantage: Difficult to create complex shapes
Hot forging and hot forging
>Benefits: Complex shapes can be created
>Demerits: Low precision, low machining speed, rough surface
Warm forging and warm forging
>It is an intermediate between cold and hot, and has each merit and demerit.
Rolling
Rolling is known as rotary forging. This is a method of deforming the material by applying pressure while rotating it. Generally, the head of a bolt is subjected to press forming. The threads are formed by rolling. We provide products for cold forging and cold forging.
Material of cold forging
Metal materials used in cold forging and cold forging are mainly as follows.
Cu copper-based metals
Copper is the second most electrically conductive metal at room temperature (1: silver Ag, 2: copper Cu, 3: gold Au), and is available at relatively low cost among highly electrically conductive metals. As a result, copper is widely used as an electrical contact terminal for forging and forging. In order to strengthen the basic functions of copper as described above for the purpose, a variety of copper-based alloys are used for forging and rolling.
Pure copper
It contains no alloying elements other than copper Cu and has the original high-conductivity of copper Cu, but its strength is inferior to other copper alloys. To prevent hydrogen embrittlement, which is a weak point of tough-pitch copper, tough-pitch copper (C1100) is used to detoxify impurities that inhibit electric conductivity while leaving 0.02 to 0.05% of oxygen remaining. Oxygen-free copper (C1020) is used in forging and forging processes to remove impurities to the limit and improve purity.
Copper alloy
Copper Cu and zinc Zn, also known as brass. As the percentage of zinc-bearing Zn increases, the hardness increases, while the brittleness also increases. Because alloying elements can be adjusted to provide machinability suitable for various press forming processes, they are used not only in electrical parts, but also in forging and press-forming parts for large automotive parts, building materials, etc. C2600 (copper Cu70%, zinc Zn30%) and C2700 (copper Cu65%, zinc Zn35%) are mainly used.
Phosphor bronze
A type of bronze made by adding tin Sn and a small amount of phosphorus P to copper Cu. Because of its strong mechanical strength and spring properties, as well as its superior wear resistance and no magnetism, it is used in forging and press-forging parts such as springs, switches, and gears in many electronic devices.
Other copper alloys
Corson alloys, which are spring-loaded and have higher electrical conductivity, are also attracting attention.
Iron and iron alloys
Stainless steel
This is an alloyed steel that is resistant to rust by adding 10.5% or more of chrome Cr to the iron Fe that is the main component. The chromate contained combines with oxygen in the air and has high corrosion resistance by forming a passive film on the surface. Because of its rust-resistant characteristics, it is used as a material for automobiles used outdoors and other construction-related forged and pressed parts.
Other metals
Aluminum
Its specific gravity to iron is about 35% lightweight, and it boasts high corrosion resistance due to its good thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, and workability and oxide film in air. Because pure aluminum has low strength, it is often used as an aluminum alloy and is widely used for forging and forging parts such as rivets.
Precious metals
Precious metals such as gold and silver are mainly used as brazing materials.
Processing method of cold forged parts
In cold forging and cold forging, we manufacture forged and pressed parts by combining a "punch" that applies force directly to the material to apply plastic deformation and a "die" that receives the material to which the force is applied. There are various punches and dies depending on the shape of the material and the shape of the final purpose, and by combining them, forging and forging processes are performed as shown below.
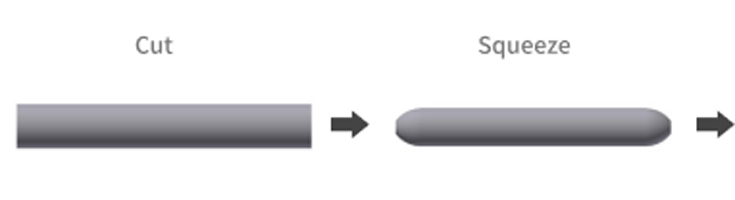
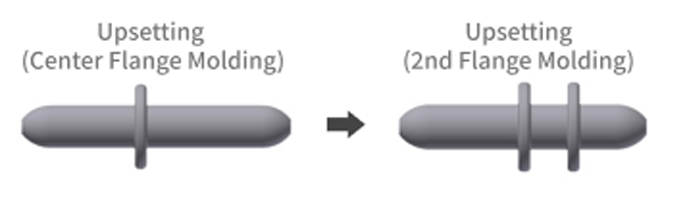
Upset processing
This is a forging and press-forming method that makes the material short and thick by tapping the material fixed with a die in the axial direction with a punch. Used to machine the head of forged and pressed parts such as rivets and bolts.
Forward extrusion
By tapping the material with a punch on a small diameter die relative to the original material diameter, the diameter of the material is narrowed down and the amount of extra material squeezed and the length of the material is increased.
Backward extrusion
When the material is placed in a die and a force is applied with a small punch against the die material diameter, the material escapes into the gap between the die and the punch, resulting in a cup-shaped shape. Used for forged parts machining and press-forged parts machining, such as caulked parts of rivets.
Cold forging and cold forging (cold header processing) Processing
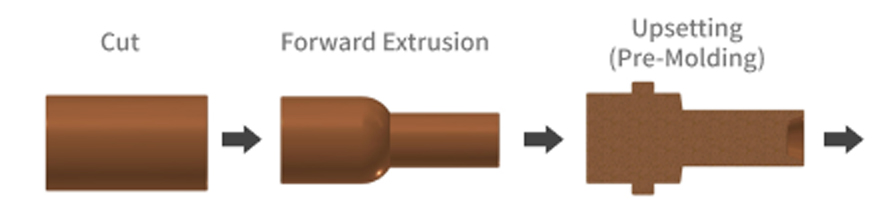

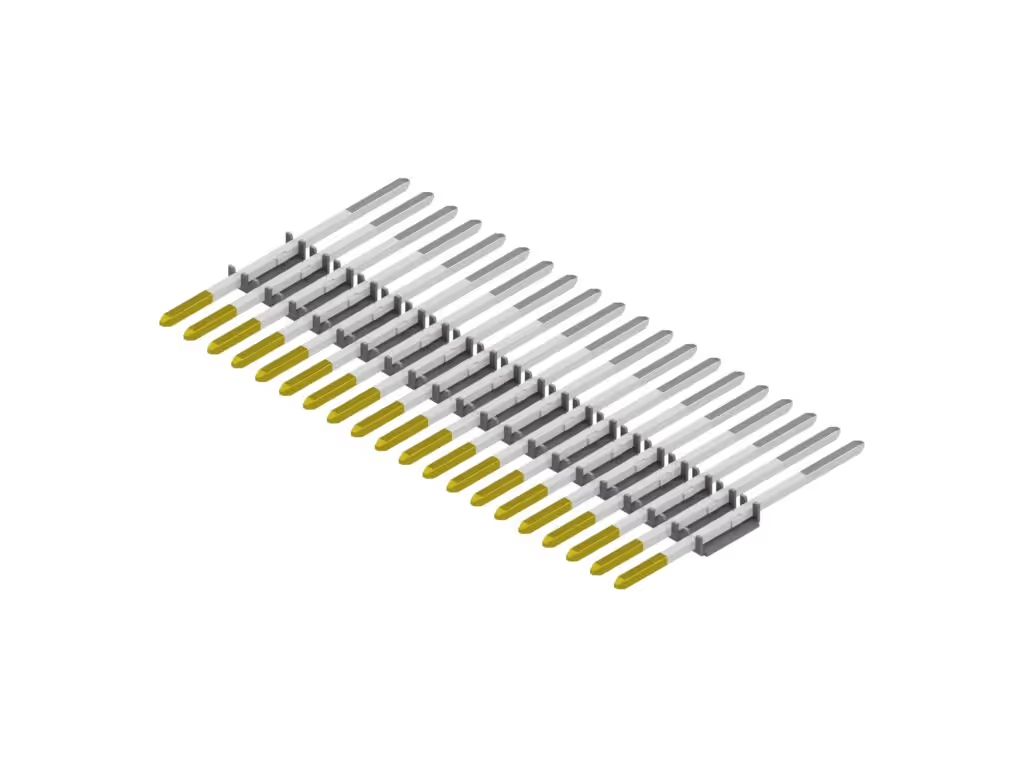
Cold forging and cold forging (cold header processing) Thin workpiece processing process
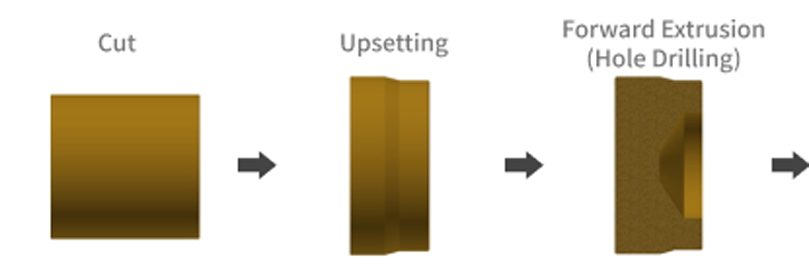
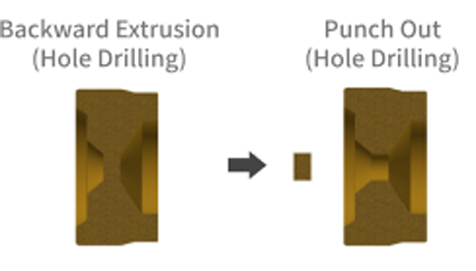
Cold forging and cold forging (cold header machining) Pin machining process with ribs
Inspection system
In recent years, the ultra-miniaturization of electronic components has led to stricter demands on various materials that make up products, the surface conditions of products, and the quality requirements for the entire product. We have introduced the latest analytical instruments to enhance our "analytical ability" and "analytical ability" so that our customers can use our products with peace of mind. We will deepen our analytical and analytical capabilities day by day to provide optimal proposals based on data.
View Evaluation Center
Use of Cold Forged Parts
Parts manufactured by cold forging and cold forging are utilized in various scenes in our everyday life by taking advantage of the characteristics of being able to produce large quantities at high speeds.
-

Electronic components
Consumer connectors, Diodes, Inspection probes, Spring connectors, Heat dissipation terminals for PCBs, Semiconductor packages, etc.
-

Automotive parts
ECU, power modules, door switches, power window actuators, headlights, taillights, microphones, alternators, rechargeable batteries, etc.
-

Fastening parts
Parts used for fastening and fixing rivets and other members
Processing machine
The FINECS Group designs and manufactures in-house forging machines and forging machines that are operated automatically to perform forging and forging, and manufactures forged parts and forging parts. In-house production of dies, such as dies and punches, for forging and forging processes also enables stable forging and forging with high precision and quality at prices that are easy to purchase.